Deploying an HAProxy on a Pacemaker Cluster

In this guide, we’ll deploy a HA-HAProxy cluster on a Pacemaker cluster.
Pre-requisites
This guide assumes you have a working Pacemaker cluster with a VIP and a web server deployed on it. See this post for a guide on how to deploy a Pacemaker cluster, this post for deploying nginx as an example web service, and this post for deploying a VIP.
All nodes
Install HAProxy
sudo dnf install -y haproxy
Dependencies resolved.
================================================================================
Package Architecture Version Repository Size
================================================================================
Installing:
haproxy x86_64 2.4.22-3.el9_3 appstream 2.2 M
Transaction Summary
================================================================================
Install 1 Package
Total download size: 2.2 M
Installed size: 6.6 M
Downloading Packages:
haproxy-2.4.22-3.el9_3.x86_64.rpm 311 kB/s | 2.2 MB 00:07
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Total 294 kB/s | 2.2 MB 00:07
Running transaction check
Transaction check succeeded.
Running transaction test
Transaction test succeeded.
Running transaction
Preparing : 1/1
Running scriptlet: haproxy-2.4.22-3.el9_3.x86_64 1/1
Installing : haproxy-2.4.22-3.el9_3.x86_64 1/1
Running scriptlet: haproxy-2.4.22-3.el9_3.x86_64 1/1
Verifying : haproxy-2.4.22-3.el9_3.x86_64 1/1
Installed:
haproxy-2.4.22-3.el9_3.x86_64
Complete!
Configure nginx to run on port 8080 as a backend
Assuming you are using the nginx example mentioned before, you can simply change the line in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf from
listen 80;
to
listen 8080;
and restart the nginx resource in Pacemaker
sudo pcs resource restart nginx
Now add the ports to the firewall
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
As said before, in production these ports should only be open to the cluster’s firewall zone.
Confgure HAProxy as a simple reverse proxy
As a start, configure /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg as:
global
log /dev/log local0
log /dev/log local1 notice
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
stats bind-process 1
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
defaults
log global
mode http
option httplog
option dontlognull
timeout connect 5000
timeout client 50000
timeout server 50000
frontend http_front
bind 192.168.30.10:80
default_backend http_back
backend http_back
balance roundrobin
server node1 node1:8080 check
server node2 node2:8080 check
server node3 node3:8080 check
listen stats
bind :9000
stats enable
stats uri /
stats refresh 30s
Ensuring that systemd does not manage the HAProxy service
sudo systemctl disable haproxy --now
Create a new resource for HAProxy
For this resource we will create a systemd resource for HAProxy, but we will disable it for now. This is so we can create a colocation constraint with the VIP resource.
sudo pcs resource create haproxy systemd:haproxy op monitor interval=10s --disabled
Cluster name: democluster
Cluster Summary:
* Stack: corosync (Pacemaker is running)
* Current DC: node2 (version 2.1.7-5.el9_4-0f7f88312) - partition with quorum
* Last updated: Sun May 12 06:06:12 2024 on node1
* Last change: Sun May 12 06:05:23 2024 by root via root on node1
* 3 nodes configured
* 5 resource instances configured (1 DISABLED)
Node List:
* Online: [ node1 node2 node3 ]
Full List of Resources:
* Clone Set: nginx-clone [nginx]:
* Started: [ node1 node2 node3 ]
* vip (ocf:heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started node3
* haproxy (systemd:haproxy): Stopped (disabled)
Daemon Status:
corosync: active/disabled
pacemaker: active/disabled
pcsd: active/enabled
Notice that the haproxy resource is disabled and stopped.
Colocate the VIP and HAProxy resources
The following command will create a constraint that will make sure the VIP starts before HAProxy as well as ensuring that they run on the same node.
sudo pcs constraint colocation add haproxy with vip
Once the constraint is added, enable the HAProxy resource
sudo pcs resource enable haproxy
You can verify that the constraint is in place by running
sudo pcs status
Cluster name: democluster
Cluster Summary:
* Stack: corosync (Pacemaker is running)
* Current DC: node2 (version 2.1.7-5.el9_4-0f7f88312) - partition with quorum
* Last updated: Sun May 12 06:10:29 2024 on node1
* Last change: Sun May 12 06:08:06 2024 by root via root on node1
* 3 nodes configured
* 5 resource instances configured
Node List:
* Online: [ node1 node2 node3 ]
Full List of Resources:
* Clone Set: nginx-clone [nginx]:
* Started: [ node1 node2 node3 ]
* vip (ocf:heartbeat:IPaddr2): Started node3
* haproxy (systemd:haproxy): Started node3
Daemon Status:
corosync: active/disabled
pacemaker: active/disabled
pcsd: active/enabled
Configure the private firewall
Allow the nodes in the cluster to reach the backend nginx servers.
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=8080/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
success
success
Configure the public firewall
In case the public http port was open before, we need to open the HAProxy port as well.
sudo firewall-cmd --add-service=http --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Configure the admin-only firewall
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=9000/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
success
success
Testing
Checking the Frontend
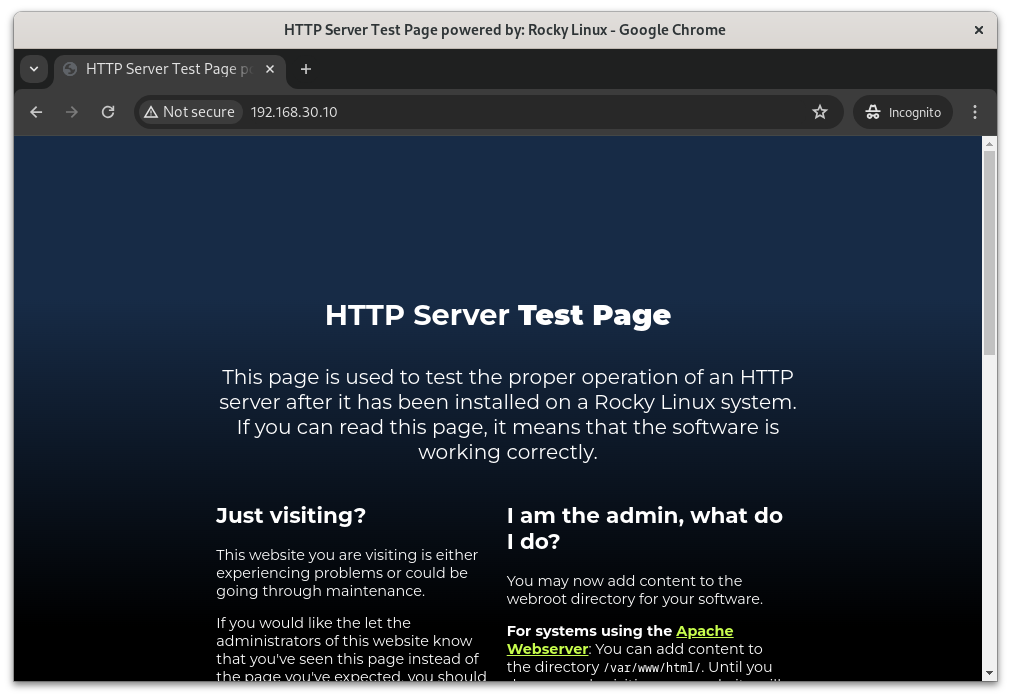
Navigate to http://192.168.30.10/ (or whatever ip/port combo you chose) to see the nginx test page.
Nginx is Alive
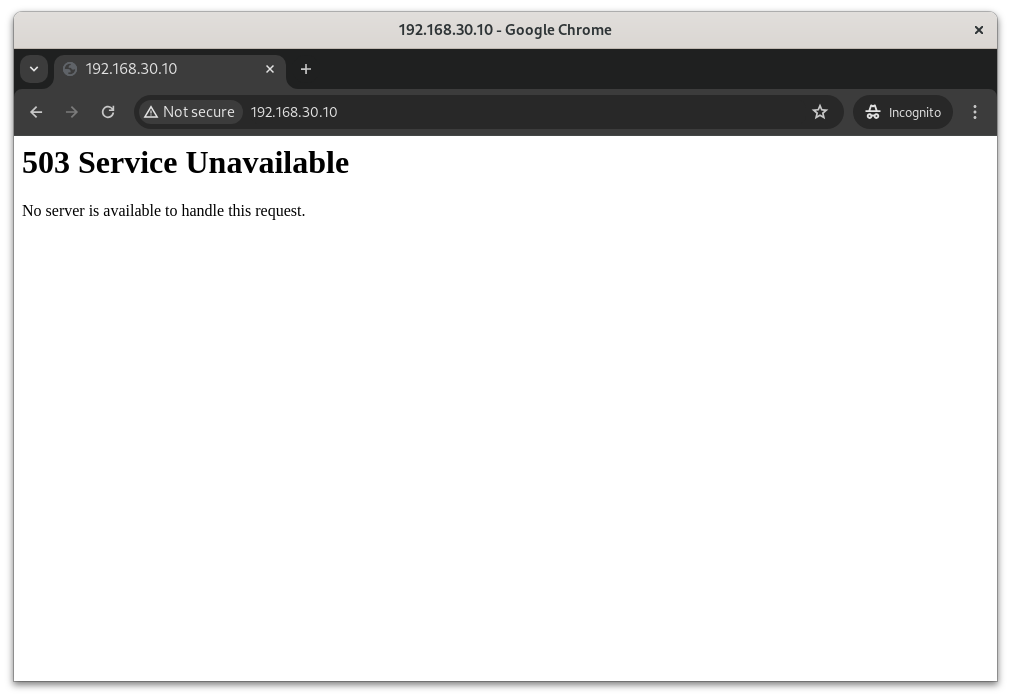
All nginx Servers are Down
HAProxy Status Page
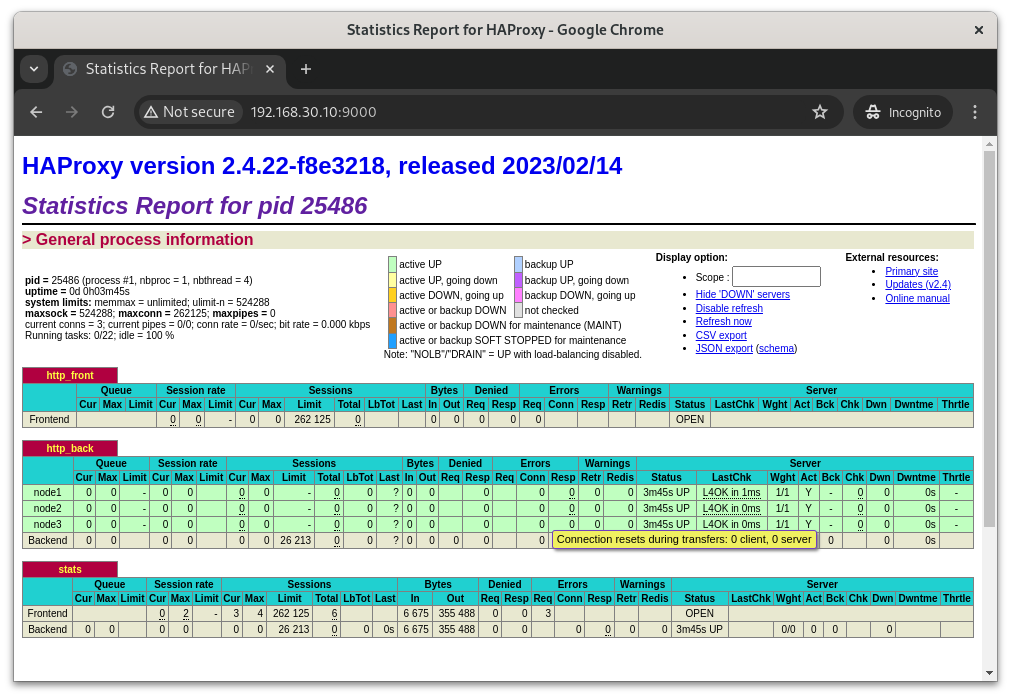
Navigate to http://192.168.30.10:9000/ (or whatever ip/port combo you chose) to see the HAProxy status page.
HAProxy Shows the Backend Servers Happy
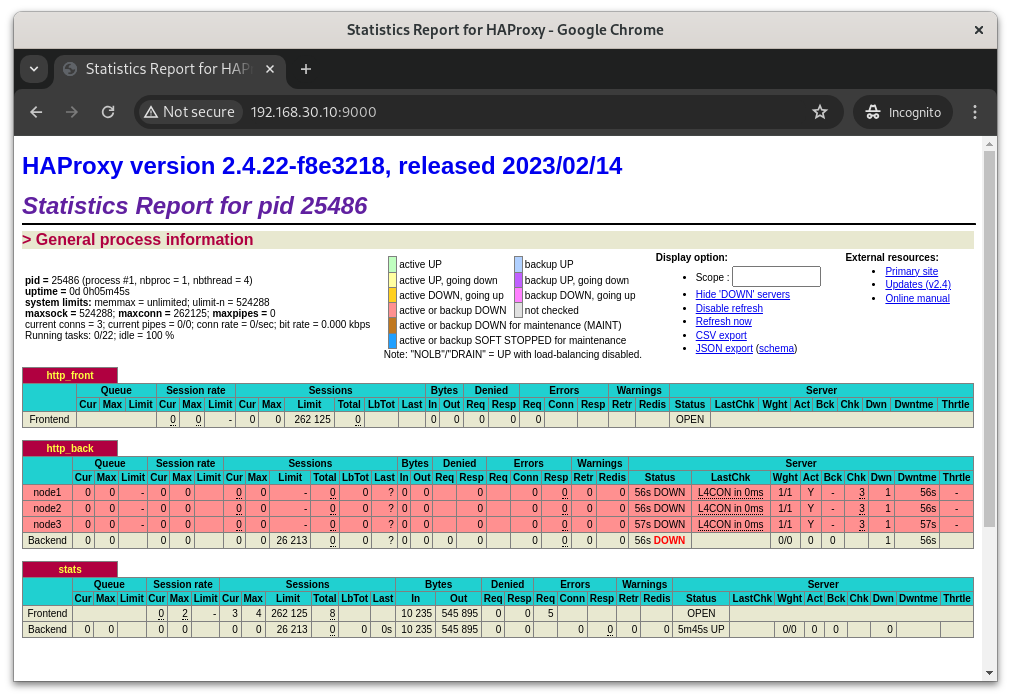
HAProxy Shows the Backend Servers Down
Related posts
pacemaker
- Deploying a VIP on a Pacemaker Cluster - 09 May 2024
- Deploying a Simple High-Availability Nginx Service with Pacemaker - 08 May 2024
- Setting up a basic Pacemaker cluster on Rocky Linux 9 - 07 May 2024